Construction
The “wave 2 energy” is an innovative project for generating zero emission electricity from sea waves. The energy production requires the installation of a structure, which is capable of converting wave energy into electricity with high efficiency. In order for this project to be successful, special attention has to be paid on the mechanism of energy harvest. In particular, the structure of the facility is an innovative idea of Glafcos Μarine and its collaborators (Mr Preftitsis & Mavromatakis). This structure has been adapted to the prevailing sea conditions in the area of interest, based on theoretical analysis and experimental studies.
Smart design
The design of the structure and its individual elements is the most important parameter for the efficient absorption of wave energy and its subsequent conversion into electrical energy. The basic structural element of the structure consists of six floaters connected by two in three pairs in an array with three axes of symmetry, which are connected to each other by the use of ligaments and joints as shown in Figure 1. That arrangement facilitates the scale up of the structure by extending it in every direction. In this way the extension will take the final form of construction which will be a cellular grid as shown in Figure 2. The ease of scalability of the facility leads to the minimization of construction costs and to the ease of its expansion. The morphology of the structure ensures the efficient absorption of energy by waves with different characteristics, such as their direction, their wave length and their height.
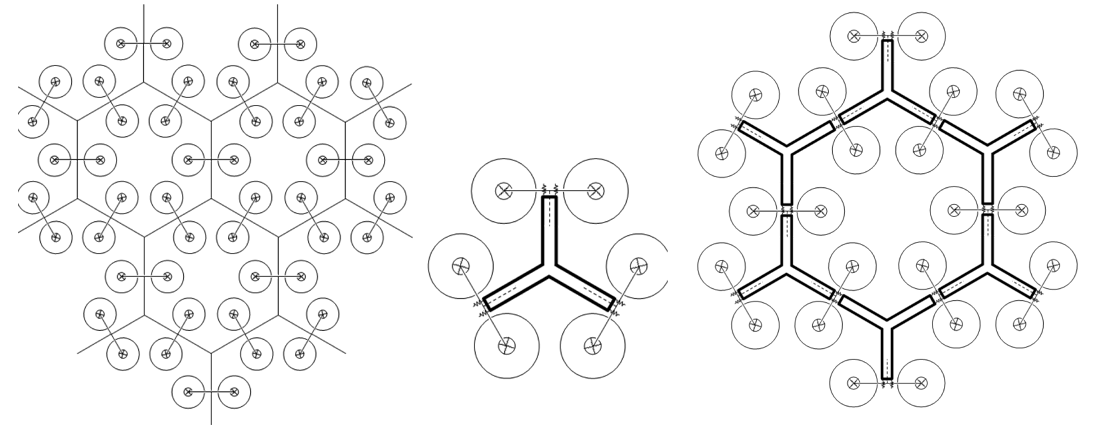
The facility is designed to absorb wave energy in three different ways depending on the height and frequency of the wave. In the case that it operates in sea conditions with small wave heights and high frequency the absorption of energy is achieved by the relative movement of the floaters. In the case of medium height and frequency waves the individual parts of the hive are considered as individual floats and the absorption of energy is carried out by the intermediate joints. Finally, in waves with high altitude and low frequency the whole cell is considered as a single floater and the absorption of energy is done by the connecting elements of cells.
Optimized components
Due to the aforementioned importance of the platform’s structural elements, we conclude that it is necessary during the design stage of the facility to pay special attention to the study of the floaters as well as the joints because the absorption of the wave energy depends on them. In particular, the design of the floaters is of great importance since they affect the functionality of the facility and the absorption of energy mainly in the small ripples. For this reason an extensive study has been conducted for the selection of the most suitable shape and material, based on experimental studies. In parallel, we have performed structural optimization based on mathematical models for the kinematics and dynamics of the platform, through many numerical studies and simulations.
Fully automated protection mechanism and durability
Finally, we have considered the possibility of immersing the construction under the surface of the water by filling with water the tanks of the floats in extreme weather conditions, which can be achieved automatically with the use of sensors and proper control software. This way the construction will be protected from extensive stress, giving the facility a longer lifespan.
